Table of Contents
The Leverage in Forex Trading Explained – Definition & Examples
As soon as you start trading Forex, you will quickly encounter the terms leverage and margin. Very few beginners have dealt intensively with the two terms in advance, although it is immensely important to know what is hidden behind a lever and the margin.
The following article will give you an overview of the leverage and margin, as well as the advantages and disadvantages using practical examples.
The leverage of trading in the Forex market simply explained
In addition to the term leverage, many brokers often use the English term leverage (stands for leverage or leverage). The leverage in trading as such is comparable to the leverage from physics. If a large weight is to be moved, a lever can be used, which means that only a small amount of force is required to move a large weight. The process is similar in the Forex market.
If leverage is used when trading foreign exchange, a large amount of money can be moved in the respective market with the help of little equity. Due to the high leverage effect, comparatively high profits can be achieved, but the risk of loss is just as high. If only one’s own free capital were used for the trades, the possibility of making high profits is severely limited. But where does the high capital used for such a leveraged trade come from?
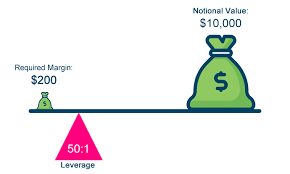
The brokers or banks that enable forex trading do not only act as an interface to connect the various players in the market. Another central task, which is taken over by banks and brokers, is the financing of trades. Above you will find a screenshot of how a leverage can be placed with the broker.
I have summarized the important facts about the lever for you in a nutshell:
- Trading with leverage is widely used in the Forex market, i.e. the use of borrowed capital when executing trades
- By using leverage, a multiple of equity can be moved in the market
- Comparatively high profits can be achieved through the leverage, but the risk of loss is comparatively high
- When trading, brokers require that a minimum amount in percentage is held as collateral (margin)
Forex Leverage: Explanation with Example
For an even better understanding of how a lever works, the following example is used:
Most start trading in the Forex market with a maximum deposit of 1,000 euros. If exactly these 1,000 euros are invested in trading currencies without the use of leverage, the 1,000 euros changes analogously to the change in the market.
Angenommen, der Trader ist mit den 1.000 Euro in das Währungspaar EUR / USD eingestiegen, bei einem Kurs von 1,20 Dollar zu einem Euro. Damit ein Gewinn von 10 Prozent erzielt werden kann, muss der Kurs auf 1,32 steigen. Eine Veränderung des Kurses ist allerdings in einer Größenordnung von 10 Prozent in einem kurzen Zeitraum sehr selten, meist benötigt der Kurs dafür mehrere Monate oder sogar Jahre. Zentralbanken haben generell ein großes Interesse, an einem möglichst stabilen Kursverhältnis bzw. an keinen überproportional hohen Schwankungen.
An dieser Stelle kommt der Hebel zum Einsatz, damit in einem absehbaren Zeitraum auch von Tradern ohne ein Kapital in Millionenhöhe ein ansehnlicher Gewinn erzielt werden kann.
Der Hebel kann dabei in den verschiedensten Größenordnungen vom Broker angeboten werden. Kleine Hebelgrößen sind u.a. 1:10 oder 1:50, größeren Hebelgrößen wiederum 1:100 oder 1:500. Wählt der Trader den Hebel 1:100 aus, kann er durch Einsatz seiner 1.000 Euro Eigenkapital mit 100.000 Euro im Markt handeln. Die 100.000 Euro entsprechen damit einem sogenannten Lot (Standard-Positions-Forexgröße).
Verändert sich der Kurs des EUR / USD, nachdem ein Long-Trade geöffnet wurde, um 1 Prozent nach oben im Markt, hat sich das Eigenkapital in Höhe von 1.000 Euro auf 2.000 Euro verdoppelt. Die Bewegung kann allerdings genauso in die entgegengesetzte Marktrichtung verlaufen. Fällt der Kurs beispielsweise um 0,5 Prozent, sind nur noch 500 Euro Eigenkapital übrig.
Anbei dazu eine Übersicht mit dem erforderlichen Kapital (Margin) bei der dazugehörigen Hebelwirkung:
Risiko minimieren bei hohen Hebelwirkungen
Durch den Hebel von 1:100 handelt der Trader mit 100.000 Euro im Markt, das Eigenkapital beträgt allerdings nur 1.000 Euro. Die Chance, einen hohen Gewinn erzielen zu können, sind dadurch zwar hoch, das Risiko eines Totalverlustes ist allerdings zu jeder Zeit genauso hoch.
But how can the high risk be reduced? The risk can be minimized by, among other things, using only part of the equity for the trade. Here is another example to illustrate the procedure.
Example of risk mitigation when applying leverage:
Of the available 1,000 euros, only 500 euros are used for the trade, the rest remains on the account for further trades. The 500 euros are then used to purchase half a Forex lot in the market, i.e. 50,000 currency units. If the price now moves by 1 percent, this results in a profit or loss of 500 euros.
Attention!
The use of a high leverage usually quickly leads to so-called “gambling”. Therefore, use the instrument carefully.
If you want to further reduce the risk, you can, for example, choose only a quarter of the money for the trade. As an alternative, a smaller lever can also be used, e.g. 1:50.
The use of a high leverage usually quickly leads to so-called “gambling”. The existing margin is quickly used up and the open trade is forcibly liquidated. As a result of the forced liquidation, the entire stake is lost. But what is margin anyway?
My tip: No more trading Forex with high fees at GBE Brokers
- Multi-regulated online broker
- German branch in Hamburg
- Over 500 different markets (stocks, ETFs, CFDs, forex, crypto)
- Forex from 0.0 pip spread (+ €3 commission)
- Fastest order routing
- PrivateGerman Service
- Client Funds Protection
- Only €500 minimum deposit (PayPal, credit cards & more)
- My rating: (5 / 5)
The margin when trading with leverage
As already described above, only a small amount of equity is necessary to move many times over in the Forex market with leverage. The remaining amount is financed by debt capital provided by the broker. In these cases, the equity invested is referred to by experts as margin. The margin thus represents the maximum amount that can be lost on a trade.
If you use 1,000 euros of equity in a trade and the price moves in the opposite direction into the loss zone, a forced liquidation will be carried out with a loss of 1,000 euros including fees. The forced liquidation of the trade protects you from losses that exceed your equity.
The risk of an associated total loss of equity increases with increasing leverage size. For example, with a leverage of 1:200, half of a move in the market is enough to result in a total loss than with a leverage of 1:100. It is precisely this risk that is often overlooked, so it is necessary to always keep in mind the high risk. In addition, there should always be a clear strategy for the trade.
Planning the trade and setting the stop loss
It is advisable to open a trade with a high leverage in the Forex market only as soon as there is a clear and strong signal that speaks for a movement in the desired market direction.
A strong signal can be a formation on the chart, such as a triple top or a triple bottom, in conjunction with other indicators.
In addition to the optimal entry into the market, a stop loss is also of great importance for trades with leverage in order to avoid the total loss of the invested capital in the worst case. For example, the stop used can be placed closely above a strong resistance on a short trade or below support on a long trade. When placing it, it should always be noted that the stop is not set too generously, due to the high leverage. The smallest movements in the market have a big impact on your equity or forex margin.
Restriction of trading in leveraged products in the EU
Trading with leveraged products is increasingly restricted in the European Union for private traders. The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) is responsible for regulating and restricting trading in currencies and contracts for difference (CFDs). The reasons given by the authorities for the restrictions are primarily the lack of knowledge about the risks of private traders via leveraged products, as well as the associated high risk of loss.
Drastic restrictions were first imposed in 2019, limiting leverage to a maximum usable magnitude of 1:30 when trading CFDs of major currency pairs. Other currency pairs may only be traded with a maximum leverage of 1:20. In addition, Eurozone brokers are not allowed to facilitate trades in the spot market. Trading CFDs in the Forex market means that a trade does not involve the real acquisition of the currency, but a financial product that reflects the performance of the currency. Thus, CFDs fall into the category of derivatives.
In concrete terms, the regulation means that trading with leverage in the Forex market is only possible for private investors via CFDs. If you want to trade the main currencies, including the euro, US dollar, Japanese yen and pound, you can do so with a leverage of 1:30. All other currencies, such as the Danish krone, may be traded with a maximum leverage of 1:20.
However, there is an exception so that higher leverage can be used again, even by private individuals. As soon as proof is provided to the broker that there is trading experience, the broker can raise the leverage size to professional level.
A confirmation from a broker with whom you have already traded for a longer period of time can serve as proof. If no required proof can be provided, the first year can usually only be traded with a small leverage. You can find more information about this in my article “Forex brokers with high leverage”.
Trading with small leverages
If you do not have the opportunity to trade with the large leverages, profitable trading is still possible. However, the risk does not decrease significantly, but the potential rewards do so all the more.
Tip:
Read my article on Forex brokers with high leverage without ESMA to be able to use high leverage as a private trader.
With the 1,000 euros of equity already considered in the course of the article, a maximum of 30,000 euros can be leveraged, which can be used for trading in major currencies.
Unfortunately, the restrictions imposed by ESMA are not specifically designed to minimize risk. The restrictions make it more difficult for traders with little capital in particular to profit from forex trading. Other means would have been needed to minimize the risk of loss.
Means of minimizing the risk of loss
Insofar as the risk of loss of inexperienced traders is in the foreground, information and the associated education on how to limit losses are particularly effective. One possibility is to enforce the use of a stop loss as a mandatory requirement. Any broker could easily integrate the mandatory requirement into the existing systems. The stop-loss should always be used in trading, detached from the current regulations. With consistent implementation, the loss of many traders is significantly limited.
Example of a mandatory application of the stop loss:
Suppose a trader wants to open a trade in the EUR/USD currency pair, with a leverage of 1:100. Since the broker requires the entry of a stop loss as a prerequisite, no trade can be opened without a stop loss. As soon as the stop loss has been activated in the input mask for placing the trade, the order will be executed in the market. With this measure, a large number of beginners are noticeably helped.
Regardless of this proposal, since 2019 the regulation has been adopted by all affected brokers who have to implement the regulation. In the meantime, however, the larger brokers have sought alternative options. Brokers who have branches outside the Eurozone offer services from these locations to clients within the Eurozone. This allows brokers to circumvent the applicable regulations. An example of this is a registered office of a broker in the United Kingdom, where the regulations do not apply.
Conclusion: Trading with leverage in the Forex market
A basic requirement is definitely that all traders understand the opportunities and risks of leverage in trading. First of all, I recommend that you start with a free demo account so that all functions and the strategy can be tested when trading without risk of loss. In order for you to practice trading and applying leverage in real conditions, MetaTrader should always be used, preferably in version 5. The download link of the MetaTrader can be found via the website of the respective broker. As soon as you have gained the relevant experience and feel confident, you can switch to a real money account.
For any trade, the use of a stop loss is an essential condition for limiting losses. In this context, a clear trading strategy should always be followed and precise planning of the trade should be done in advance.
If you do not trade professionally in the markets and have another main profession, a leverage of no more than 1:100 should be chosen. You wonder at this point, why only a leverage of 1:100? The trade is usually closed only after a few hours over the course of the day. Due to the volatility, a tight stop loss is not recommended, otherwise it is usually triggered far too quickly.
However, if you trade more professionally and can follow the trade, a higher leverage is a good chance to optimize profits.
It is important that you find a strategy that suits you, a combination of several different strategies is of course also possible. A strategy that is time-consuming, but works very well with high-leverage sizes, is Forex scalping. When scalping, a tight stop loss is always recommended.